We are happy to announce that our FlexChess pilot case at Cardiff University in the UK has achieved a significant milestone with publications. See a summary below of the papers:
“Flexibility from industrial production processes is of great importance to supporting low-carbon power grid, especially when it is enhanced by the flexibility of battery energy storage via forming a Virtual Energy Storage System (VESS). The pilot site and use case studies in the UK in FlexCHESS are about utilizing flexibility of industrial processes via VESS. The below are our latest research in this area, published as two papers in the conference proceedings of IEEE EI2 2023 China and IEEE ISGT EUROPE 2023 France.”
Pengfei Su, Yue Zhou, School of Engineering, Cardiff University
Smart Scheduling of Electric Arc Furnace Steelmaking Processes
More and more UK steel plants are moving towards electric arc furnace (EAF) steelmaking to decarbonise the UK steel industry. However, the nature of the EAF steelmaking process is highly electricity-intensive, leading to high electricity consumption and corresponding electricity costs, directly affecting steelmakers’ operational costs and profitability. For example, the electricity costs of UK steelmakers can represent up to 180% of their Gross Value Added (GVA). One viable solution involves smart scheduling of EAF steelmaking processes to reduce electricity costs by taking advantage of the time-varying electricity prices and renewable energy generations.
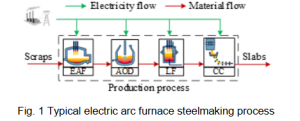
The typical EAF steelmaking process, as illustrated in Fig. 1, consists of four stages, including EAF, Argon Oxygen Decarburization (AOD), Ladle Furnace (LF), and Continuous Casting (CC). Existing studies have mathematically formulated the steelmaking process using the resource task network approach to capture the essential scheduling requirements. Based on the current research foundation, we bridge two gaps with respect to granularity restrictions in batch production and incomplete consideration of price incentives.
1.Overcome granularity restrictions in batch production for flexibility provision
Integrating the complementary capabilities for flexibility provision of steelmaking loads and battery energy storage systems (BESS) can improve overall responsiveness. More specifically, steelmaking loads offer large but discrete power adjustments due to batch production mode. In contrast, BESS offers smaller but continuous power adjustments due to high investment.
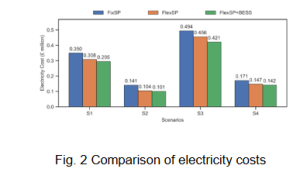
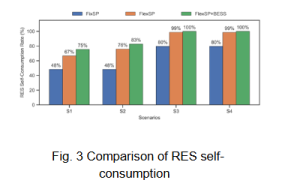
To address granularity restrictions in batch production, we propose a coordinated demand response strategy for EAF steelmaking processes, incorporating BESS to address granularity restrictions and harmonise the time scales of electricity prices, renewable energy power predictions, and batch steel production mode. Compared to the case with the scheduling objective of make-span minimisation (FixSP), the proposed case (FlexSP+BESS) effectively reduces electricity costs by up to 28.7% (Fig. 2) and improves the utilisation of renewable energy by up to 35% (Fig. 3) by leveraging BESS to enhance responsiveness to electricity price fluctuations and renewable energy availability.
2.Demand response considering multiple components of the electricity bill
Steel plants can engage in price-based demand response to reduce electricity costs, but there is often low awareness of the network charges for optimal scheduling. UK steelmakers pay around 30 times higher network charges than their immediate competitors. Shifting loads to lower price periods can create new peak demands, increasing network costs. The increasing integration of renewable energy also raises the importance of capacity-based bill components. Therefore, we aim to develop an optimal scheduling model for the steelmaking process that comprehensively considers all electricity bill components.
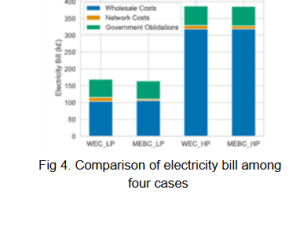
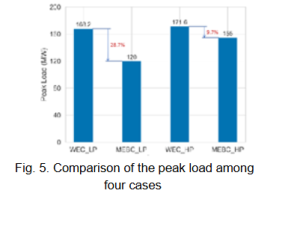
Numerical case studies show that the proposed model reduces both the electricity bill and peak load, outperforming strategies based solely on wholesale prices. Specifically, it achieves an up to 3.1% decrease in the electricity bill (Fig. 4) and an up to 28.7% reduction in peak load (Fig. 5). The growing penetration of renewable energy sources indirectly increases network costs due to grid investments, underscoring the importance of our comprehensive approach in reducing end-user billing.
Reference:
- Su and Y. Zhou, “Optimal Scheduling of Steelmaking Process Considering Multiple Electricity Bill Components,” 2023 IEEE 7th Conference on Energy Internet and Energy System Integration (EI2), Hangzhou, China, 2023, pp. 4287-4291, doi: 10.1109/EI259745.2023.10513013.
- Su and Y. Zhou, “Demand Response from Steelmaking Process Coordinated with Energy Storage Systems,” 2023 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Europe (ISGT EUROPE), Grenoble, France, 2023, pp. 1-5, doi: 10.1109/ISGTEUROPE56780.2023.10407210.
